 HuiTong
HuiTong  2025-06-13
2025-06-13
In recent years, domestic labor costs have greatly increased, and Party A's requirements for construction period are getting higher and higher. Saving time means saving costs! Hydraulic quick hitch are gradually being recognized and widely accepted. In the past, it took more than 40 minutes for two people to replace accessories such as breakers. Today, it only takes 30 seconds. Are you not a time-saving helper?
Hydraulic quick hitch for excavators are also called quick-change connectors and quick connectors. The quick connector can quickly install and switch various configuration parts (bucket, ripper, breaker, hydraulic shear, etc.) on the excavator, which can expand the scope of use of the excavator, save time and improve work efficiency.
Let's understand the difference between the next two generations of hydraulic quick hitch.

First generation hydraulic quick hitch
The universal hydraulic quick hitch is currently the most widely used connection method on the market, and it is also the main product type developed by many manufacturers. According to the different working principles, the universal quick change device can be subdivided into manual, semi-automatic and fully automatic (including hydraulic wrist) and other forms.
1. Manual quick change device
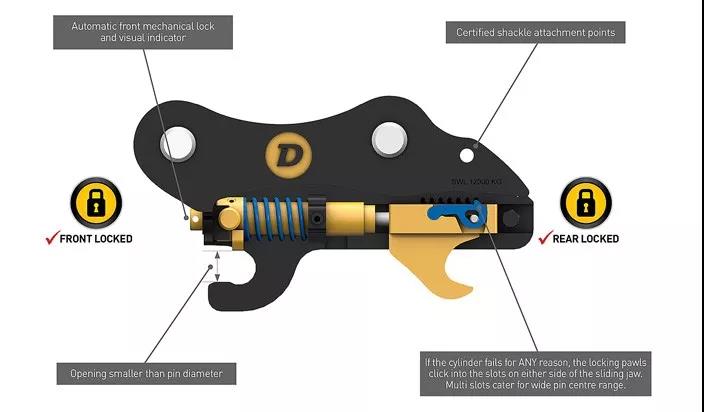
The structure of a typical manual quick-change device is shown in the figure below. Generally, the front lock hook is fixed and integrated with the body of the quick-change device. The movable rear lock hook can have various forms, such as a linkage mechanism ( Use the dead center position of the mechanism), spring lock tongue or tighten bolts, etc. to complete the connection and lock with the attachment. When in use, the coupling mechanism is required to be manually operated by the operator. After the connection between the attachment and the lock hook is completed, the safety pin must be manually inserted to lock to prevent accidental fall of the implement.
2. Semi-automatic quick change device
Most semi-automatic quick-change devices have the same structure and principle as manual ones. However, a hydraulic piston rod is used instead of manual operation to control the connecting lock hook. Therefore, the operator does not need to leave the cockpit, but can complete the attachment by operating the button. Coupling and locking of tools and quick-change devices. Common semi-automatic quick-change devices have two types: hook type and latch type.
3. Ordinary automatic hydraulic quick hitch
The so-called full-automatic quick-change device is to improve the work of the semi-automatic quick-change device that requires the operator to insert the safety pin into an additional safety spring device that uses an oil cylinder to drive and install a hydraulic lock. The operator can complete all attachment replacement work in the cockpit.

In quick change devices, an independent safety mechanism is usually used to ensure that the coupling and locking mechanism is in a fully closed position, and there is a special indicating device in the cockpit to determine whether the locking mechanism is fully engaged with the attachment.
The ordinary automatic quick-change device, through the double protection of hydraulic and mechanical, makes the replacement of attachments more convenient and safe. As far as the products used in the current project are concerned, there are mainly two types: single-claw locking type and double-claw locking type.
The development direction of the first-generation quick-change connector products is mainly focused on further improvements in safety, reliability, easy operation, and compact structure.
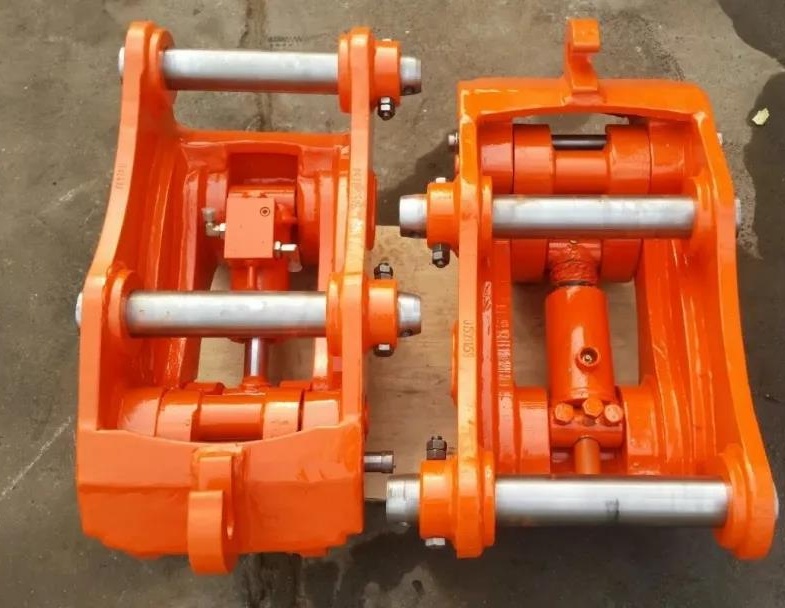

Second generation quick change device connector
Since the first-generation quick-change device did not increase the number of degrees of freedom of the excavator's working arm (that is, the flexibility of space movement and posture), it limited the excavator's more functions.
Therefore, the second generation of hydraulic quick hitch (also known as multifunctional hydraulic wrists) has appeared. This type of device increases the flexibility of the excavator, and expands and extends the functions and operating range of the host.